
SUB-1GHZ
Sub-1GHz refers to wireless communication technologies operating in the license-free ISM bands below 1 GHz (typically 433 MHz, 868 MHz in Europe, and 902–928 MHz in North America). Unlike standardised LPWANs such as LoRaWAN® or Sigfox, Sub-1GHz networks are usually proprietary — meaning companies design their protocols, modulation schemes, and network topologies to meet specific needs. It is widely used for low-power, mid-range communication where Wi-Fi or cellular is not practical.
How Does Sub-1GHz Work?
The flexibility of Sub-1GHz lies in its customizable protocol — developers can optimise for longer range, higher throughput, or lower latency depending on the use case.
1. End Devices (Sensors & Nodes)
IoT devices equipped with Sub-1GHz RF modules (using FSK, GFSK, OOK, or proprietary modulation) collect data such as temperature, motion, or equipment status. They transmit packets over the unlicensed sub-GHz band.
Example: A door sensor sends an “open/close” signal to the network.
2. Gateways / Coordinators
Depending on the network design (point-to-point, star, or mesh), devices send messages directly to a coordinator or through a gateway. The gateway aggregates data from many devices and forwards it to the backend system.
Example: A gateway in a factory receives machine status data from dozens of sensors.
3. Server / Cloud
The server processes, stores, and manages device data. It can run locally (on-premise) or in the cloud. Proprietary protocols allow flexibility in encryption, reliability, and throughput.
Example: Globiots server receives soil moisture readings every 30 minutes from farm sensors.
4. Applications
Data is delivered to dashboards, alarms, or control platforms. Users can visualise information, receive alerts, or trigger automation.
Example: A smart home app notifies the owner if a window sensor detects unusual activity.

Sub-1GHz Key Features
Sub-1GHz Applications
Sub-1GHz & Other Connectivities
Title |
|---|
Coverage Range |
Data Rate |
Power Consumption |
Device/ Service Cost |
Required Infrastructure |
Typical Applications |
Sub-1GHz | Sigfox | LoRaWAN | NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|---|
1–10 km | 3–10 km (urban), 30–50 km (rural) | 2–15 km (urban), 15–40 km (rural) | 1–10 km (excellent indoor penetration) |
Several kbps to hundreds of kbps | 100 bps uplink, 600 bps downlink | 0.3–50 kbps | 26–250 kbps |
Very low | Very low | Very low | Low to medium |
Low | Low (subscription-based) | Low | Medium (IoT SIM) |
Self-deployed network | Sigfox network | Private gateways or public LoRaWAN network | NB-IoT mobile network |
Warehouse monitoring, environment monitoring, industrial monitoring and control | Low-cost asset tracking, utility meters, simple low-cost sensors, simple alarm & monitoring systems | Smart factory, smart agriculture, smart cities, smart building, logistics tracking | Smart meters, environmental monitoring, smart parking, healthcare devices, logistics tracking |
Daviteq Sub-1GHz Sensors & Gateways
-
Advanced narrow-band wireless technology of Texas Instruments
-
Low interference
-
Ultra-low power design with 10-20 year battery life with a single battery 1.5V
-
Strong 2-way communication between sensors and coordinator
-
High penetration capability
-
Simple deployment
-
Straight-forward system architecture for easy integration to existing DCS, SCADA, PLC...
-
IP67/ 68 protection for both Indoor and Outdoor applications
-
CE mark
-
Multiple choices of sensors or I/O: temperature, humidity, pressure, level, vibration, CO₂, CO, NH₃, Cl₂, H₂S...
Sub-1GHz Sensors
Sub-1GHz Actuators
Sub-1GHz Gateways
Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
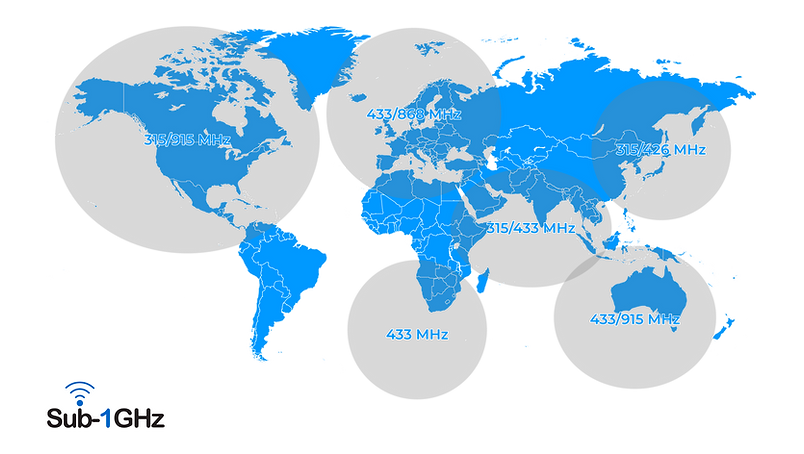
What frequencies does Sub-1GHz use?
Sub-1GHz systems typically operate at 433 MHz, 868 MHz (EU), and 902–928 MHz (US/Asia) within the ISM bands.
What modulation schemes are used?
Common choices include FSK, GFSK, OOK, 2-FSK, and DSSS, though many vendors implement proprietary schemes for optimised range and reliability.
How far can Sub-1GHz devices communicate?
The range is usually 1–10 km, depending on modulation, antenna design, and environment. Mesh topologies can extend coverage further.
What data rate is possible?
Unlike Sigfox/LoRaWAN, Sub-1GHz can support several kbps up to hundreds of kbps, making it more versatile but with higher power use.
What are the strengths and limitations of Sub-1GHz?
-
Strengths: Flexibility, no operator dependency, higher data rate, low power, and low cost.
-
Limitations: Proprietary (lack of interoperability), requires self-deployment, smaller ecosystem compared to standardised LPWANs.





